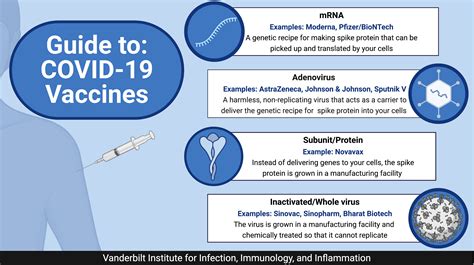
The Role of Vaccines in Health
Vaccines play a pivotal role in maintaining public health by preventing the spread of infectious diseases. They work by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight pathogens without causing the disease itself. When vaccinated, individuals develop immunity, providing personal protection and contributing to community immunity, also known as herd immunity. This collective protection is crucial, especially for those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants or individuals with certain health conditions.
An essential aspect of vaccine efficacy is their ability to significantly reduce disease incidence and transmission rates over time. To illustrate this impact, consider the data below:
| Disease | Before Vaccination | After Vaccination |
|---|---|---|
| Measles | 500,000 cases/year | 100 cases/year |
| Polio | 15,000 cases/year | 0 cases/year |
| Whooping Cough | 200,000 cases/year | 10,000 cases/year |
As seen in the table, vaccines have transformed the landscape of infectious diseases. Additionally, vaccines undergo rigorous testing for safety and efficacy before being approved for public use. For more information on vaccine safety and education resources, visit Vaccines.govor Tennessee Immunization Program. Understanding these elements is crucial for making informed health decisions that benefit both individuals and communities alike. For further insights on vaccine-related topics, see our additional resources hereand here.
How Vaccines Combat Diseases
Vaccines provide a crucial defense against infectious diseases by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens. When a vaccine is administered, it introduces harmless components of the disease-causing organism, such as proteins or inactivated parts. This process trains the immune system to identify these invaders, allowing it to mount a swift response if exposed in the future. As a result, vaccines not only protect the vaccinated individual but also contribute to community immunity or herd immunity, reducing the spread of diseases within populations. This collective protection is vital in safeguarding vulnerable groups who may be more susceptible to severe illness. For comprehensive details about vaccines and their benefits, resources like the FDA Vaccinessite offer valuable information on vaccine safety and efficacy. By understanding how vaccines combat diseases, individuals can make informed health decisions that benefit both themselves and their communities.
Understanding Vaccine Safety
Vaccine safety is a critical aspect of public health that requires thorough monitoring and research. Vaccines undergo rigorous testing in clinical trials to assess their safety and efficacy before receiving approval for public use. These trials measure the potential side effects and determine how well the vaccine works against infectious diseases. According to the World Health Organization, "The benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks." It’s important for individuals to be informed about the safety regulations that vaccines follow, which include continuous surveillance even after approval to identify any adverse reactions.
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in understanding vaccine safety by staying informed through reliable sources. For example, organizations like Children’s Hospital’s Precision Vaccines Programhelp promote awareness of vaccine research advancements. Furthermore, consulting healthcare professionals can provide personalized insights into vaccine safety for children and adults alike. Such proactive approaches foster community trust in vaccines, ultimately leading to higher vaccination rates and healthier populations. For more information on vaccine types and their histories, visit Wikipedia’s Vaccine page.
The Science Behind Vaccines
Vaccines work by training the immune system to recognize and combat pathogens without causing the disease itself. When a vaccine is administered, it introduces a harmless component of the virus or bacteria—such as proteins or sugars—into the body. This process stimulates an immune response, leading to the production of antibodies. These antibodies remain in the body, providing immunity and enabling the immune system to respond quickly if exposed to the actual pathogen in the future. Different types of vaccines, including inactivated, live-attenuated, and mRNA vaccines, utilize various methods to achieve this goal. For a deeper understanding of vaccine types and their functions, resources like CDC Vaccinesand HHS Immunization Basicscan provide valuable information. As research continues, scientists are discovering more about how vaccines can bolster immunity against evolving strains of diseases, illustrating their critical role in modern medicine and public health initiatives.
Vaccines: A Public Health Asset
Vaccines serve as a vital resource for protecting public health by preventing the spread of infectious diseases. They work by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight pathogens, significantly reducing the incidence of illnesses that can lead to severe health complications. This proactive approach not only safeguards individual health but also contributes to herd immunity, which protects vulnerable populations that cannot be vaccinated themselves. Moreover, the global vaccination efforts have resulted in the eradication or control of diseases such as smallpox and polio, demonstrating the tangible benefits of widespread immunization programs. As highlighted by organizations like WHO, maintaining high vaccination coverage is essential for continued public health advancements. For further information on vaccines and their benefits, resources like MedlinePluscan provide comprehensive insights into this critical aspect of healthcare.
Why Vaccination Matters Today
Vaccination remains a cornerstone of modern public health strategies, playing a crucial role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. With increasing global travel and interconnectedness, the potential for outbreaks of illnesses such as measles or influenza grows significantly. Vaccines not only protect individuals but also contribute to community immunity, benefiting those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons. Timely vaccinations help curb the resurgence of diseases that were once under control, ensuring that public health systems are not overwhelmed. Furthermore, by safeguarding populations against preventable diseases, vaccines reduce healthcare costs and promote healthier communities overall. As we continue to face emerging health threats, the importance of vaccination becomes even more apparent, reinforcing its critical role in promoting public health and safety.
Mechanisms of Vaccine Protection
Vaccines function by simulating an infection, which activates the immune system without causing the disease itself. When a vaccine is administered, it introduces a harmless component of the pathogen, such as inactivated viruses or pieces of their proteins. This prompts the body to produce specific antibodies and memory cells tailored to recognize and combat the actual pathogen upon exposure in the future. Additionally, vaccines can enhance the immune response by training it to respond more quickly and effectively. This proactive approach not only protects vaccinated individuals but also contributes to herd immunity, decreasing overall disease incidence in the community. By understanding these mechanisms, we can appreciate how vaccines play a crucial role in preventing outbreaks and mitigating the effects of infectious diseases.
The Impact of Vaccines on Society
Vaccines have a profound impact on society, significantly contributing to the reduction of infectious diseases. By providing immunity to individuals, vaccines not only protect those who receive them but also create herd immunity, which safeguards those who cannot be vaccinated, such as infants and individuals with certain health conditions. This collective protection helps prevent outbreaks and can even eliminate diseases within communities. Additionally, the widespread use of vaccines leads to lower healthcare costs and a reduction in the burden of disease on public health systems. As vaccination rates increase, so do opportunities for economic growth, as fewer people fall ill and require medical care. Ultimately, vaccines play a pivotal role in shaping healthier societies, fostering a sense of security among populations against potential disease threats.